PROGRAM
Conservation of the Forest Elephant in the Campo Ma’an National Park in
Southern Cameroon
PROJECT
Conservation of the Forest Elephant (Loxodonta africana cyclotis) in the Campo Ma’an National Park in Southern Cameroon through Species Status Improvement, Human-Elephant Conflict Management, Awareness, and Community Livelihood Enhancement
Project number: CMR/SGP/OP7/Y3/STAR/BD/2022/02
2022 – 2024
INTRODUCTION
Established in 1992, the Global Environment Facility’s (GEF) Small Grants Programme (SGP) is an institutional initiative implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
As part of the seventh operational phase of the GEF’s Small Grants Programme, CASuDev undertook an ambitious project in the Campo Ma’an National Park aimed at protecting elephants, reducing human-wildlife conflicts, and improving the living conditions of surrounding communities through innovative and participatory approaches.
SUMMARY
This project was a response to harmful human activities impacting the forest ecosystem of the Campo Ma’an National Park (PNCM). It contributed to rehabilitating the elephants’ habitat within the PNCM while sustainably increasing the income of local communities living near the park, with a focus on gender inclusivity.
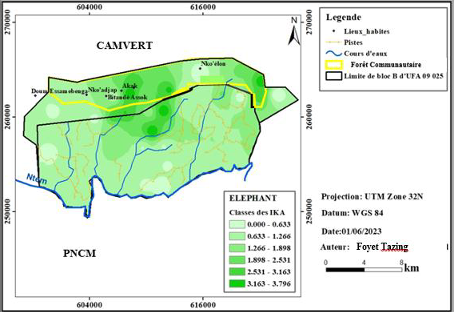
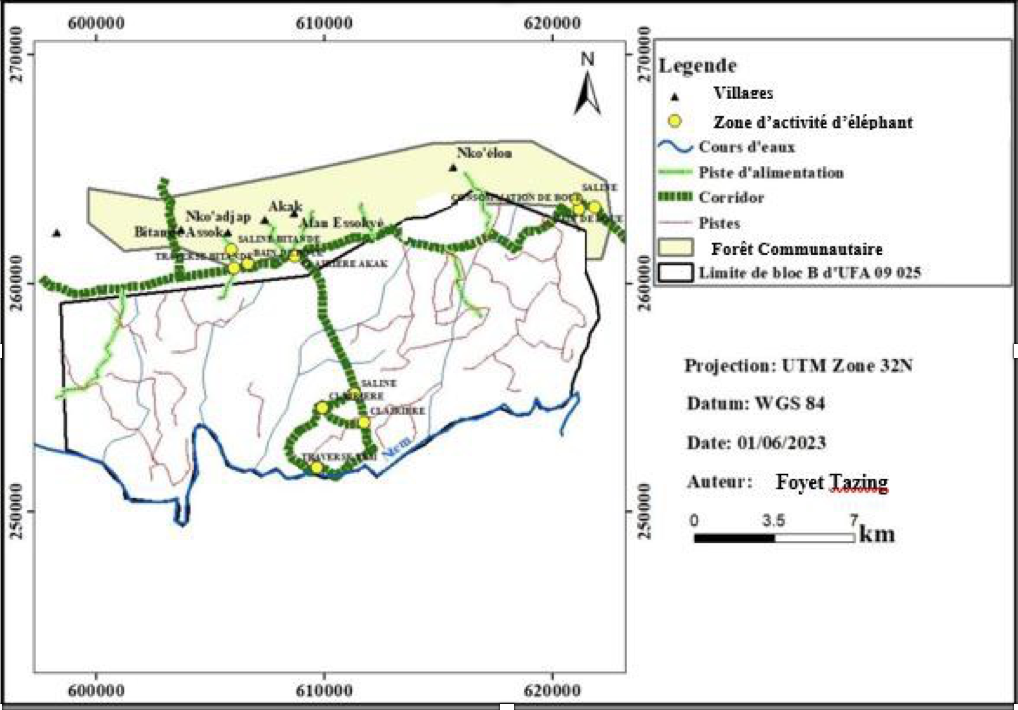
- Elephant Population Survey in PNCM: Identification and mapping of clearings, corridors, salt licks, activity zones, elephant population distribution, and visitation frequency in the western periphery of the PNCM.
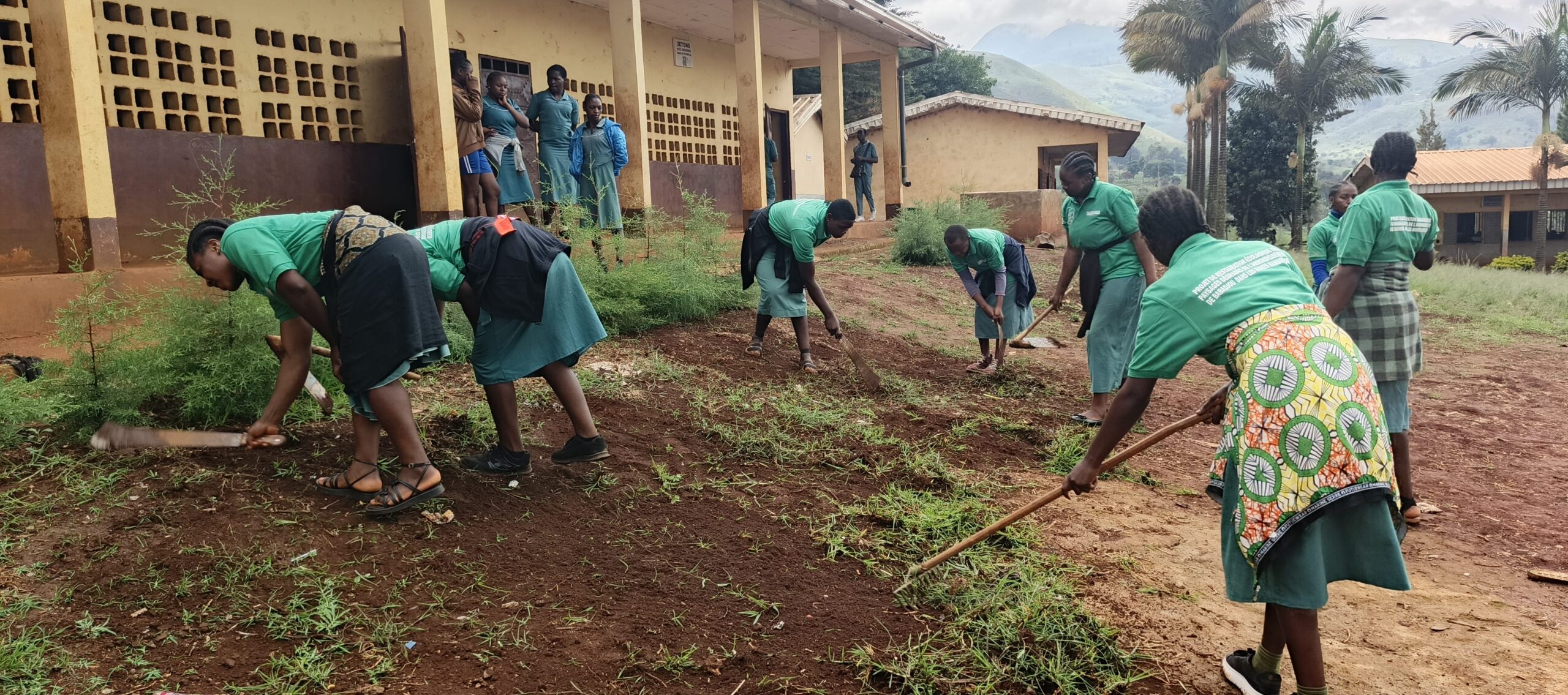
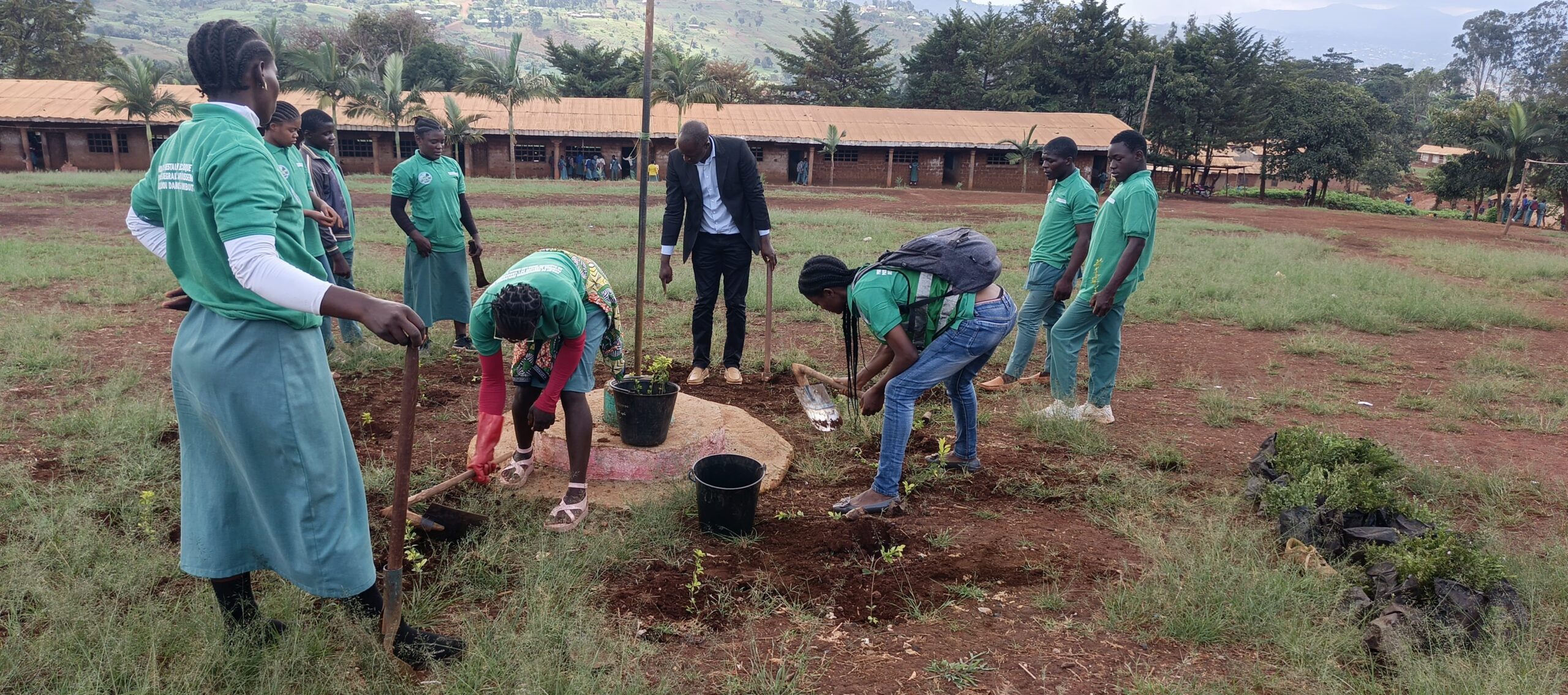
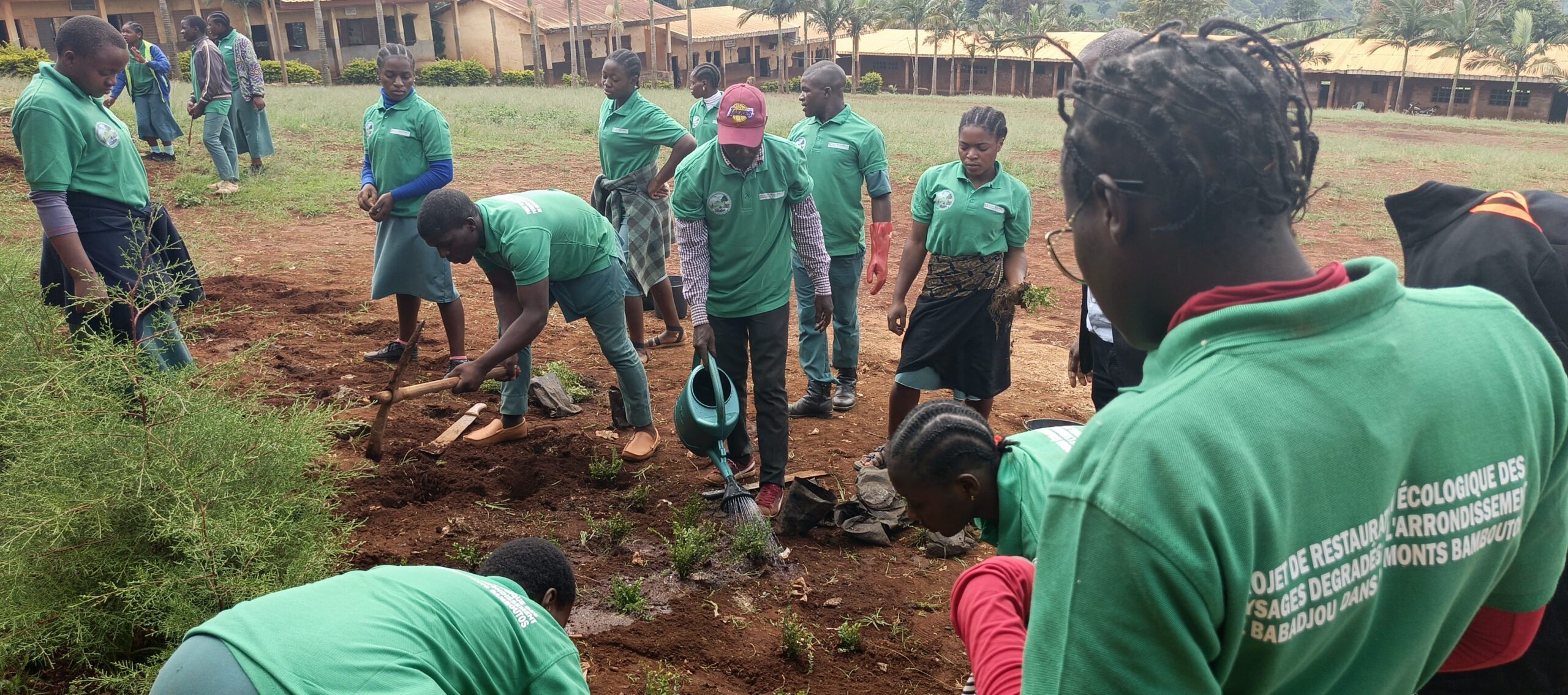
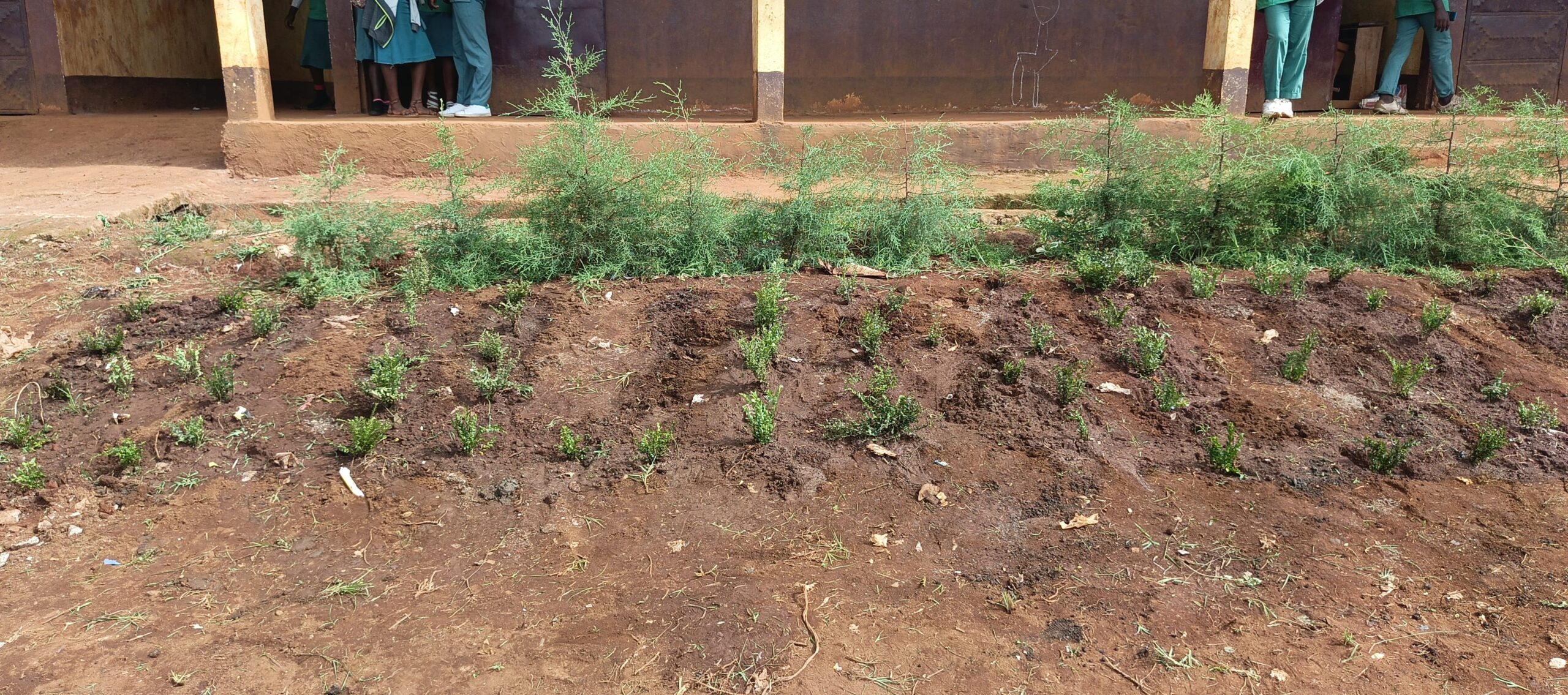
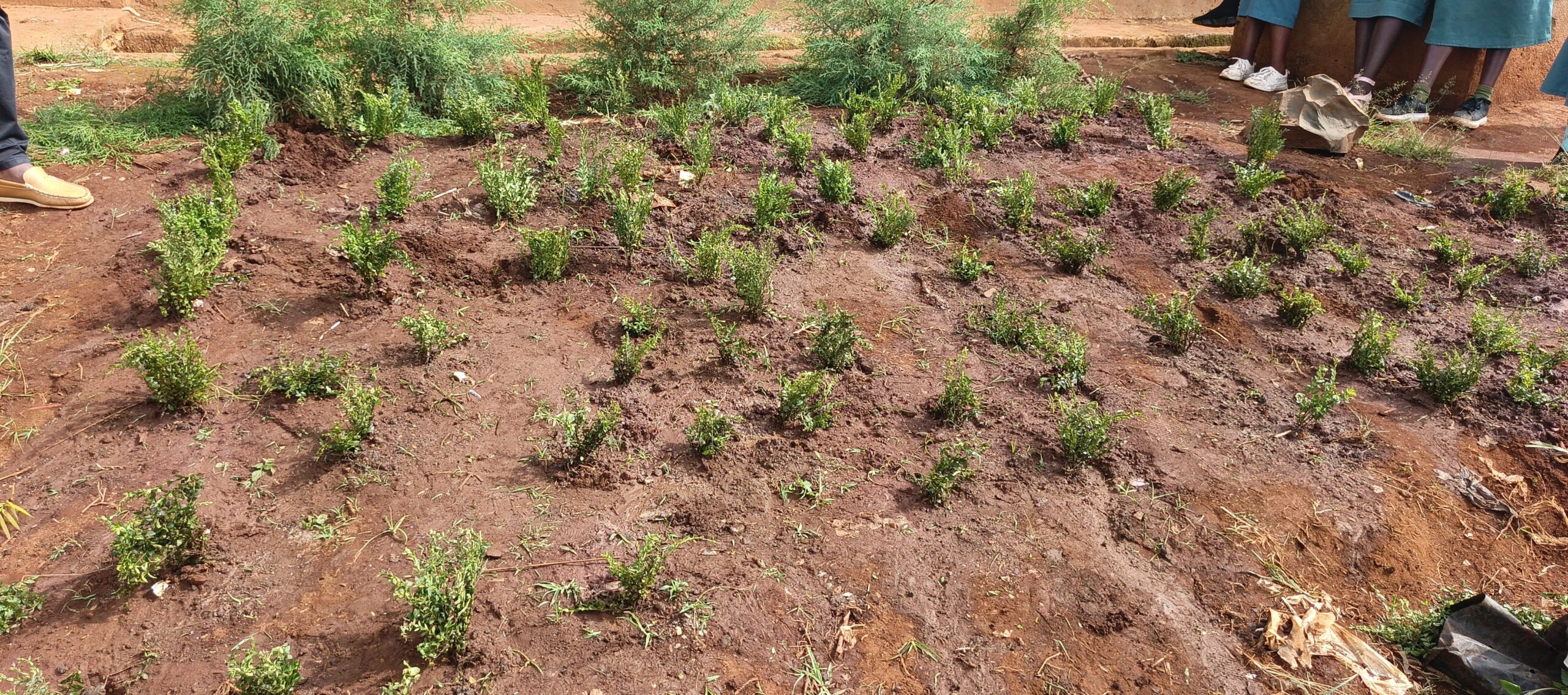
- Conservation: Rehabilitation of a clearing, a corridor, and an activity zone; wildlife monitoring; enhanced collaboration among stakeholders to reduce human-elephant tensions.
- Awareness: Direct and indirect impact on 360 local residents; youth engagement as environmental ambassadors within their communities.
- Local Economy: Capacity building for 1,200 inhabitants through honey production, cassava-based product processing, and agroforestry initiatives.
ASSESSMENT
CASuDev sought to combine applied research by involving two young engineers from the Faculty of Agronomy and Agricultural Sciences at the University of Dschang. Their thesis funding facilitated an inventory of the elephant population in the National Park and an assessment of human-elephant conflicts.
- FOYET TAZING Gabriel. 2023. Suivi de la dynamique des populations d’éléphants dans la périphérie ouest du Parc National de Campo Ma’an au sud du Cameroun. Faculté d’agronomie et des sciences agricoles : Université de Dschang.
- WANG-YANG Maaga. 2023. Etat des lieux et perspectives de mitigation des conflits homme-éléphant à la périphérie ouest du Parc National de Campo Ma’an, sud Cameroun. Faculté d’agronomie et des sciences agricoles : Université de Dschang.
MAIN OBJECTIVES ACHIEVED
Three main objectives, addressing environmental, social, and economic challenges, were established to ensure better coexistence:
Improving Elephant Conservation
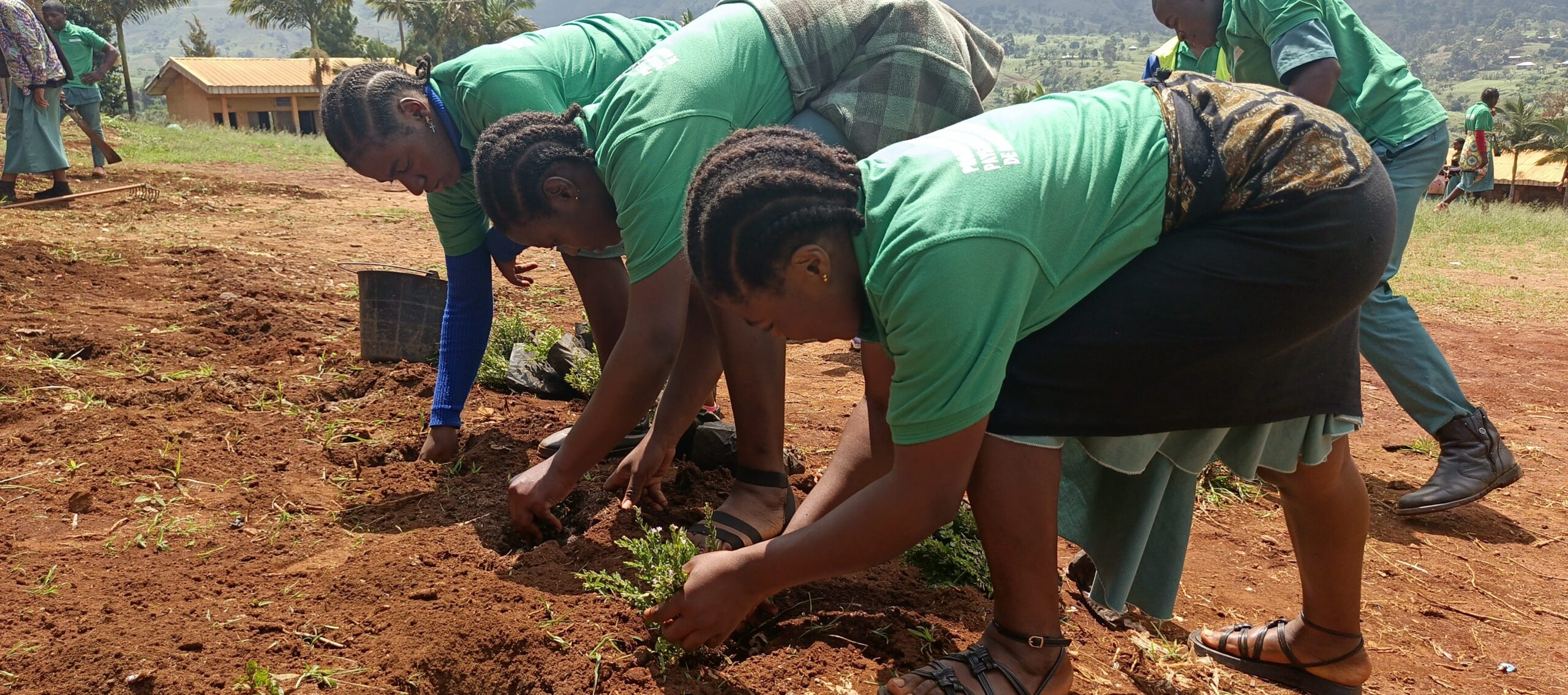
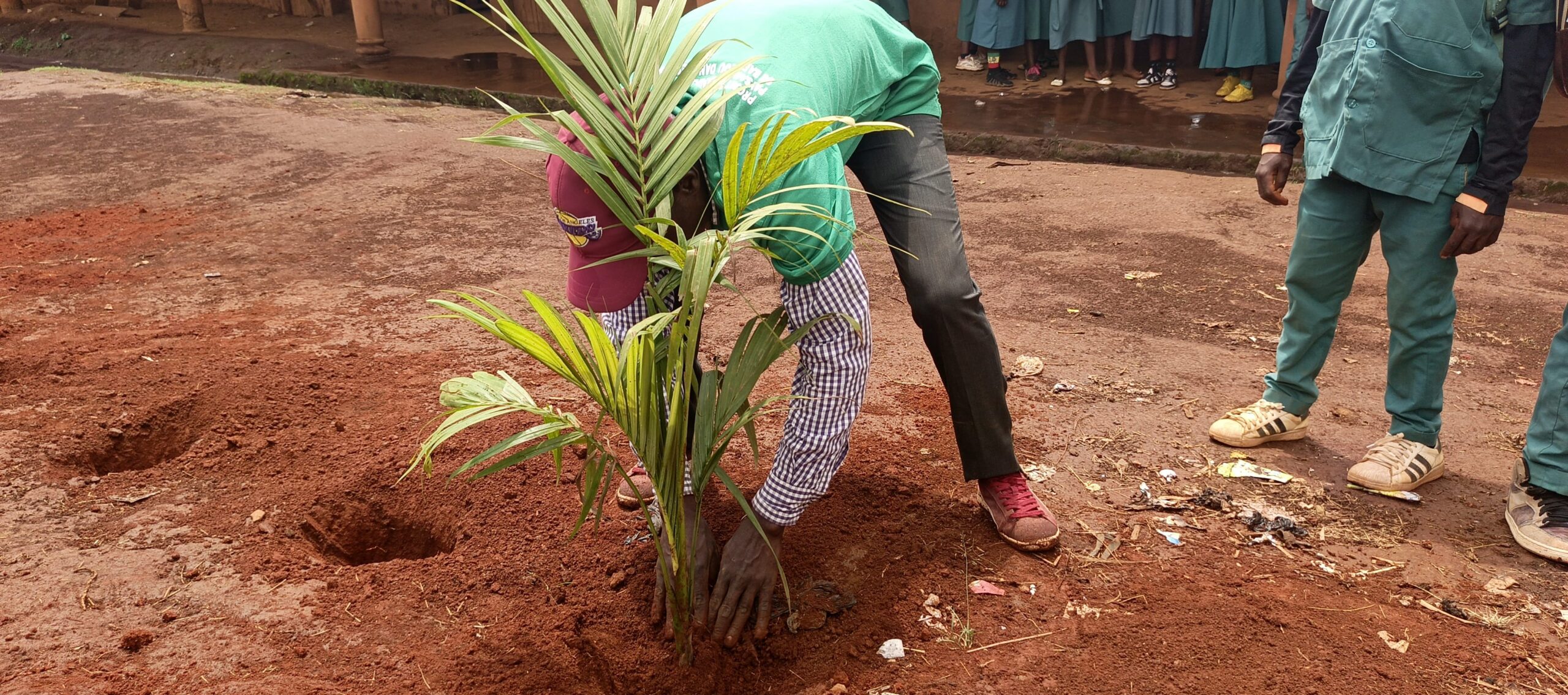
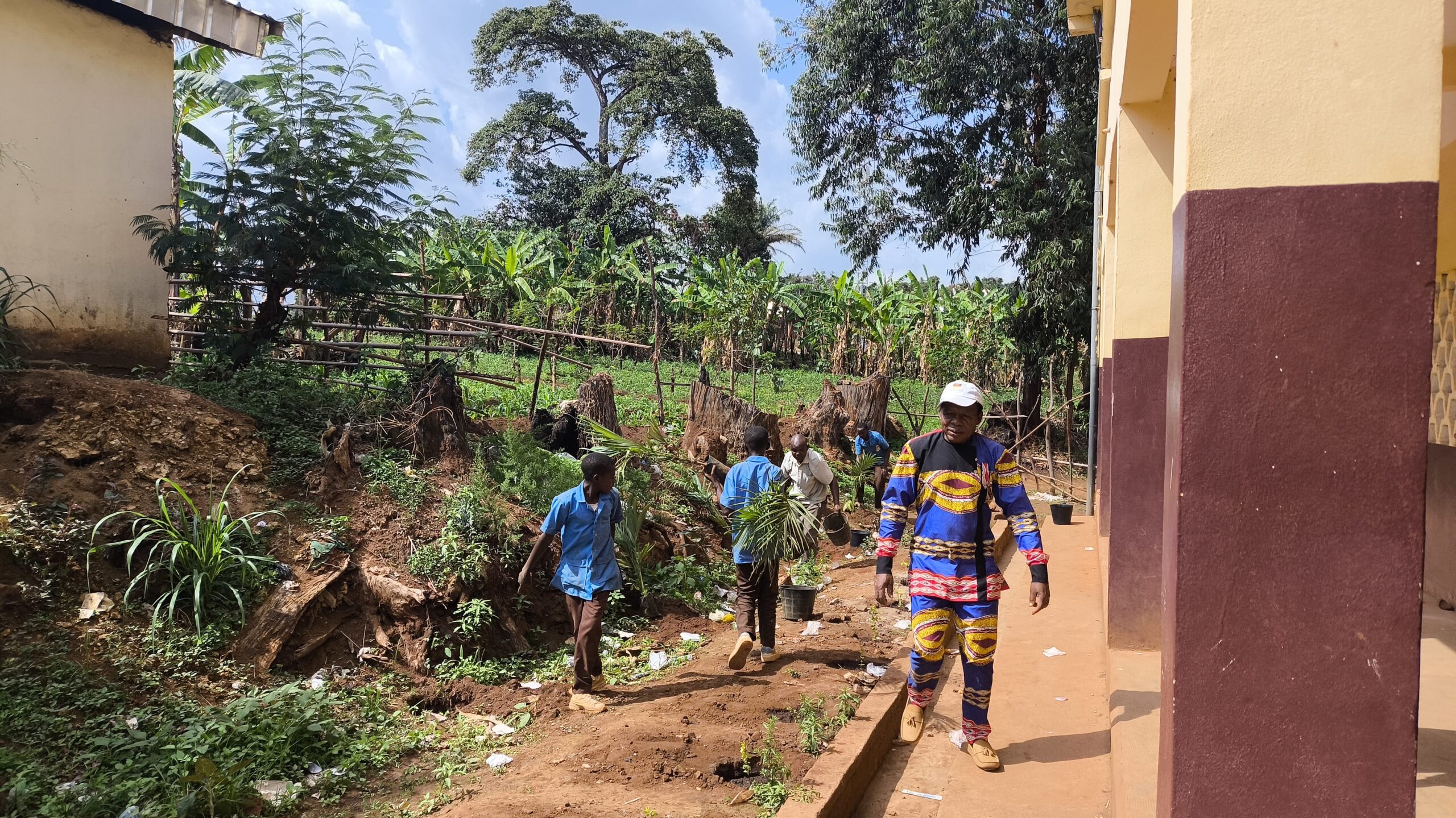
- Rehabilitation of corridors between Nkoadjap, Akak, Nkoelon, and Mvini villages to facilitate elephant movement.
- Wildlife monitoring and recommendations for government and conservation organizations.
- Exploration of technological solutions, such as camera traps, to better understand elephant needs.
- Enhanced collaboration with local stakeholders, including authorities, communities, and research centers.
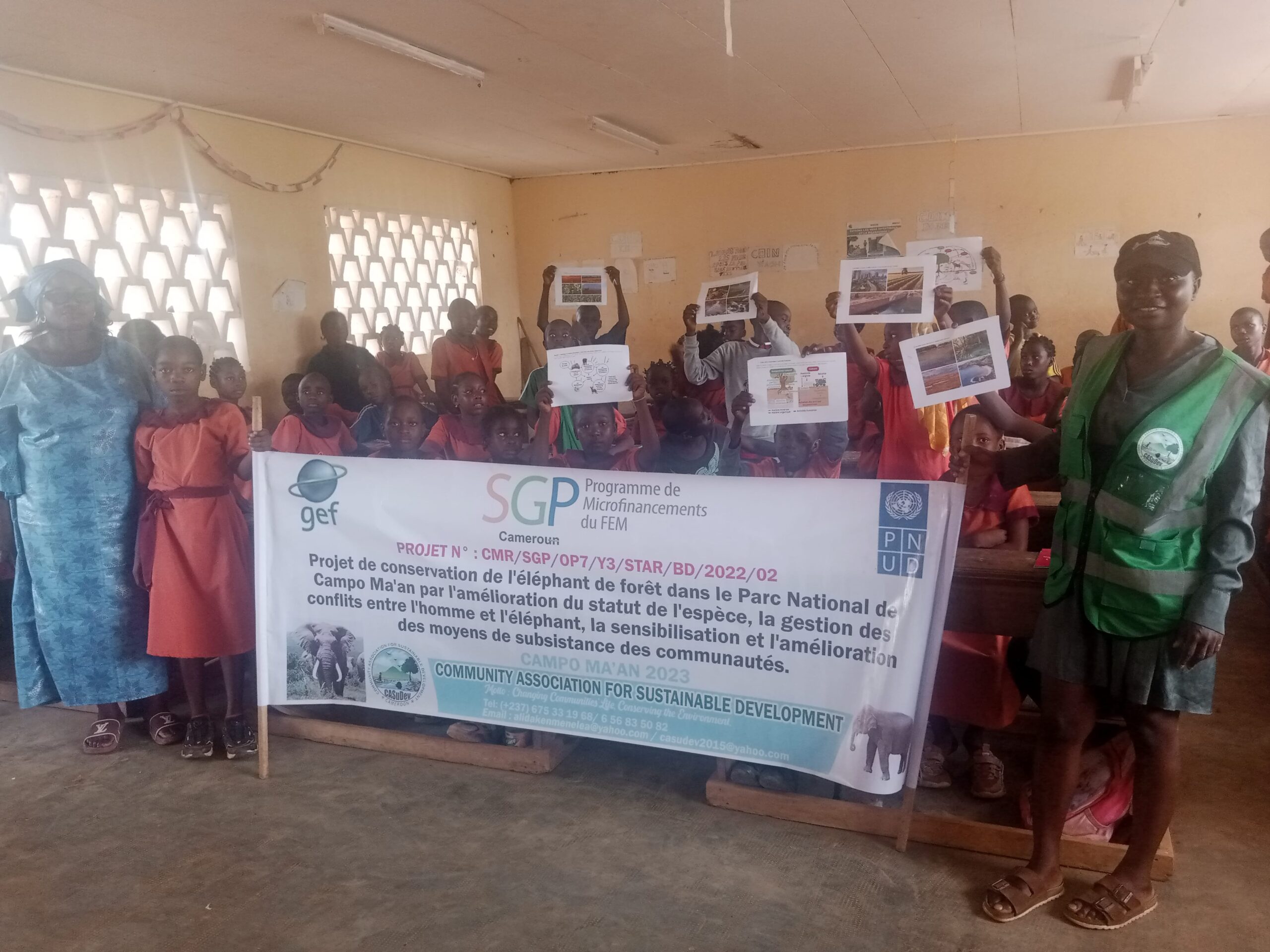
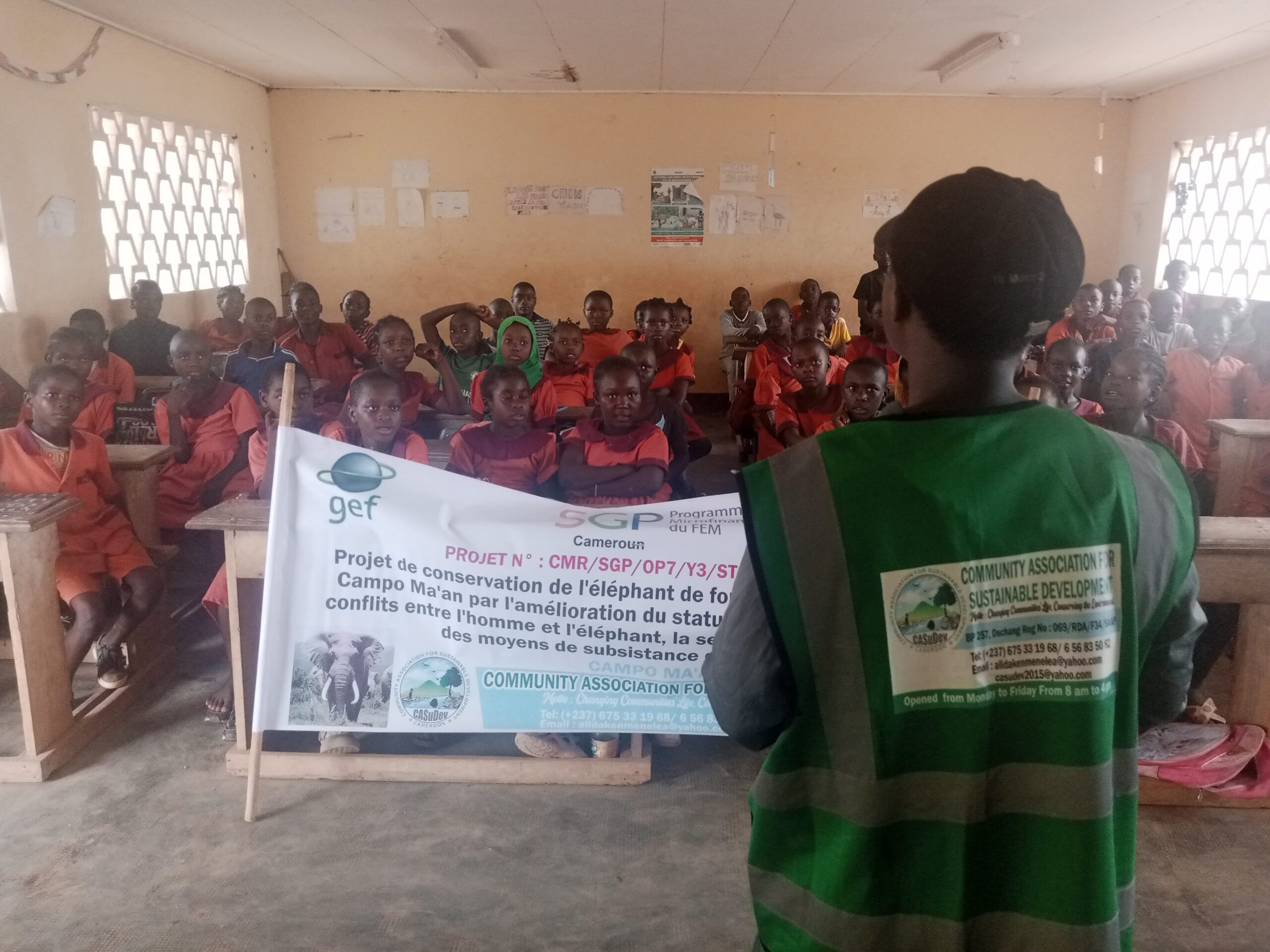
Raising Awareness Among Local Stakeholders
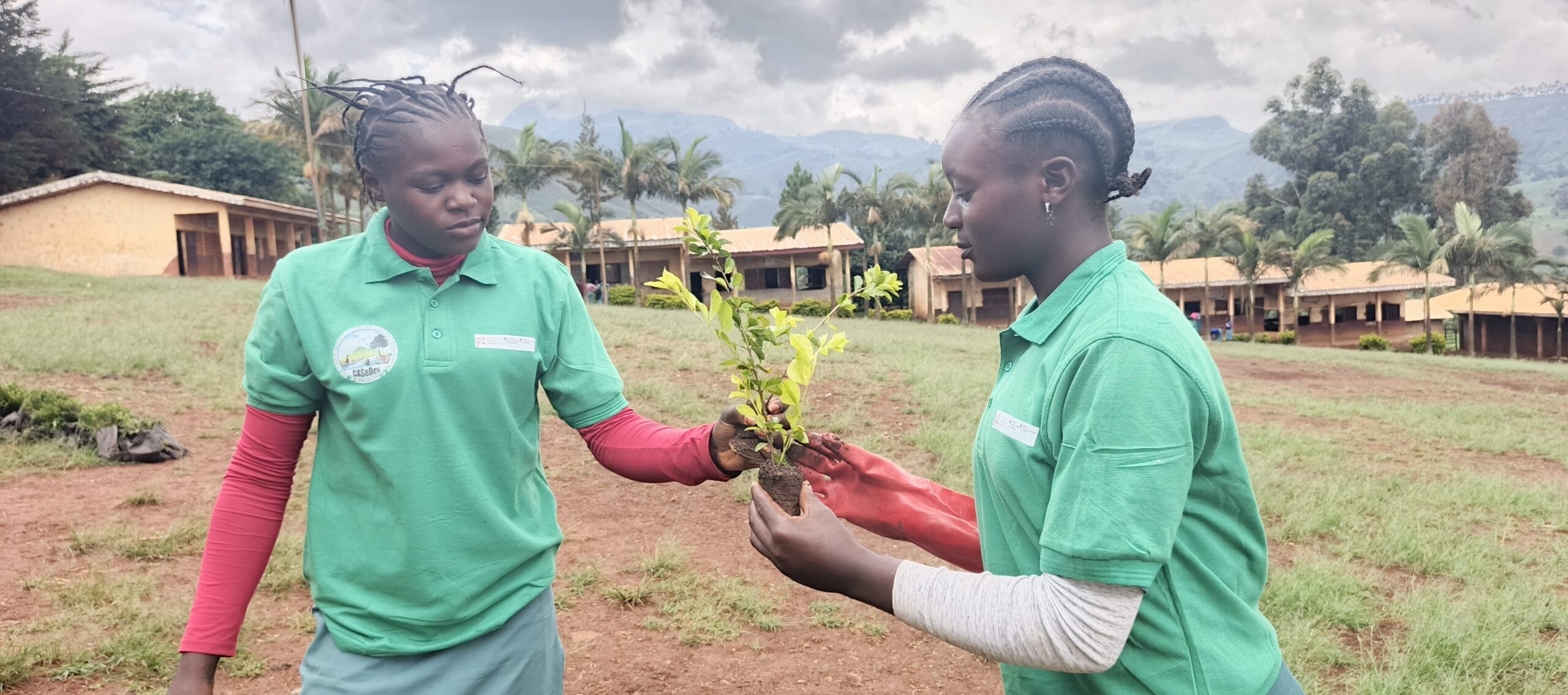
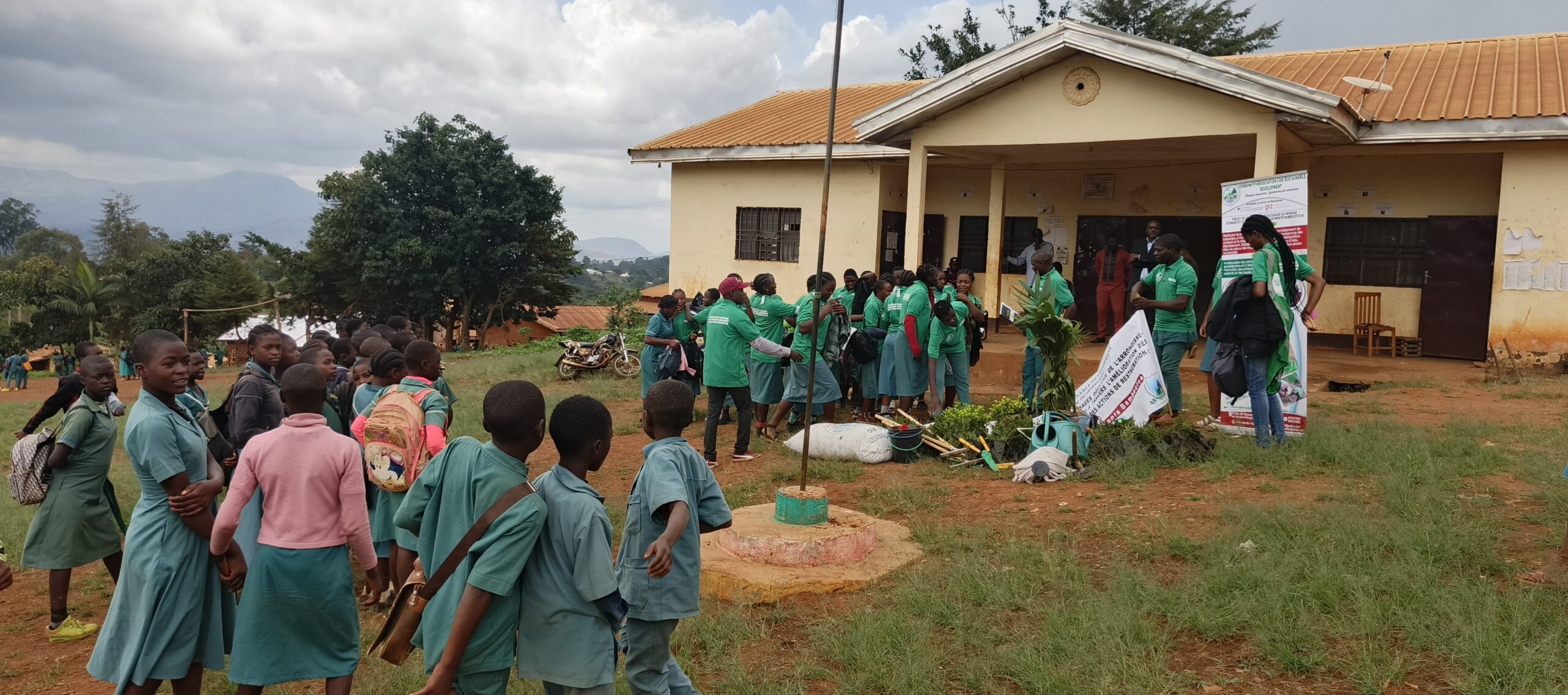
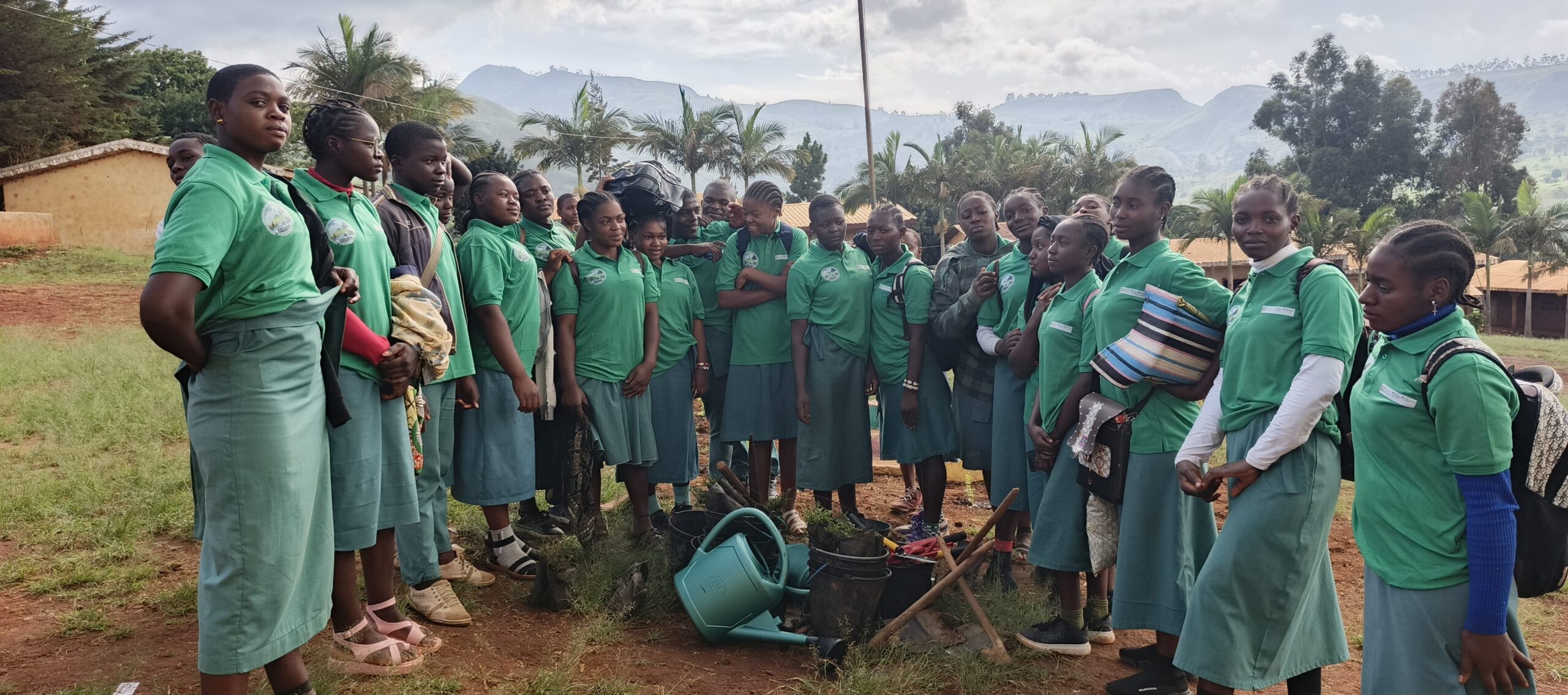
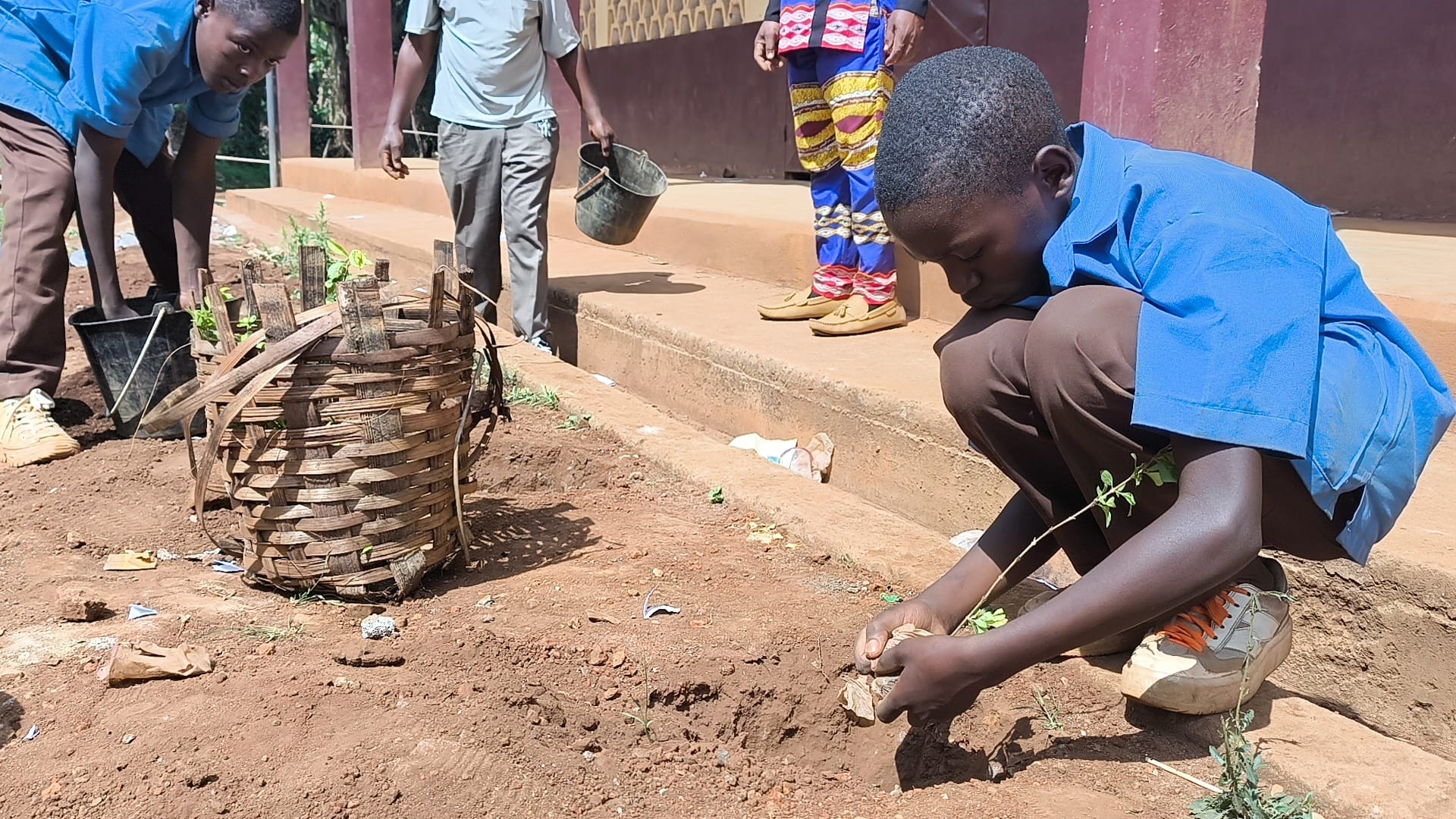
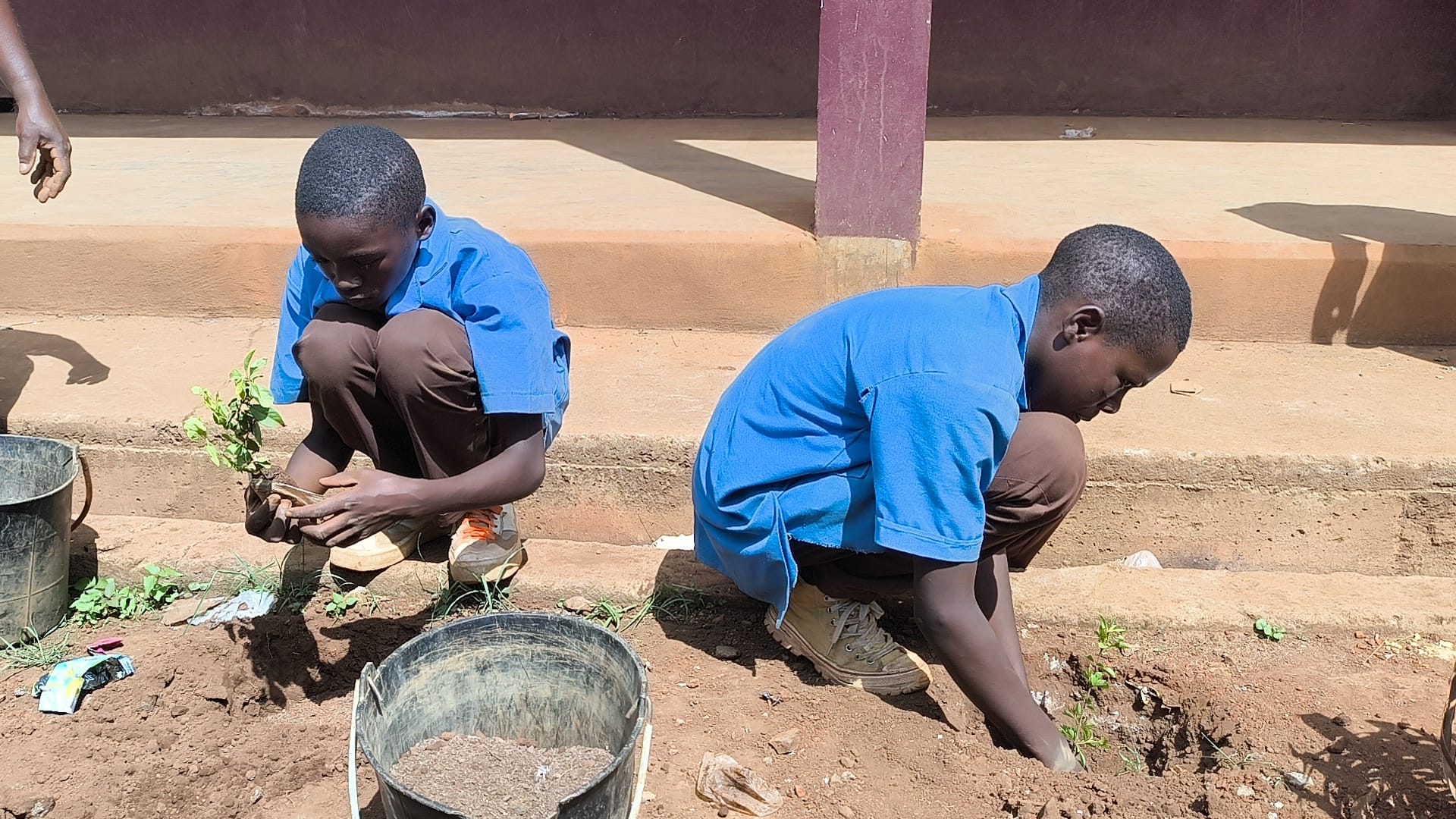
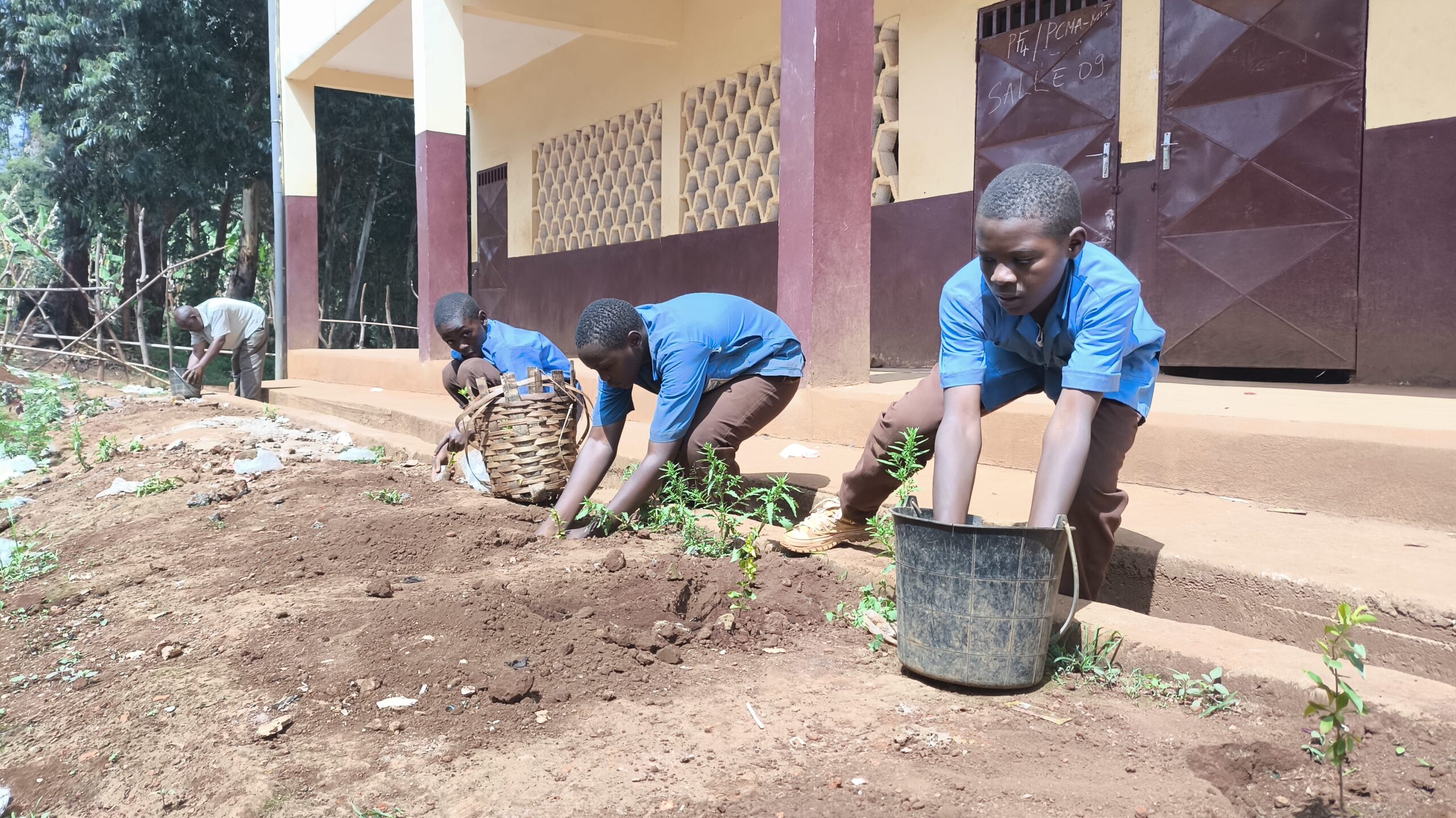
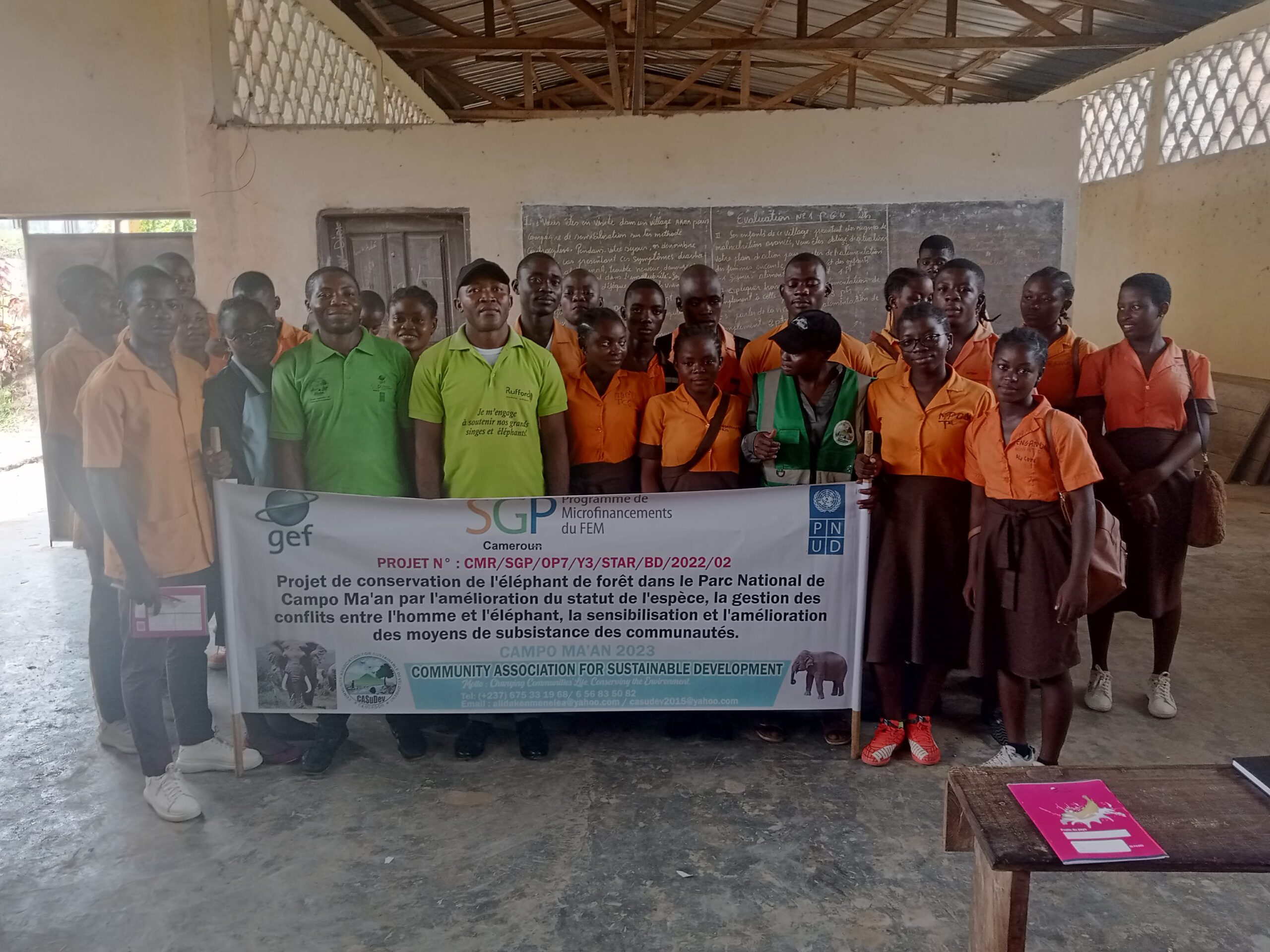
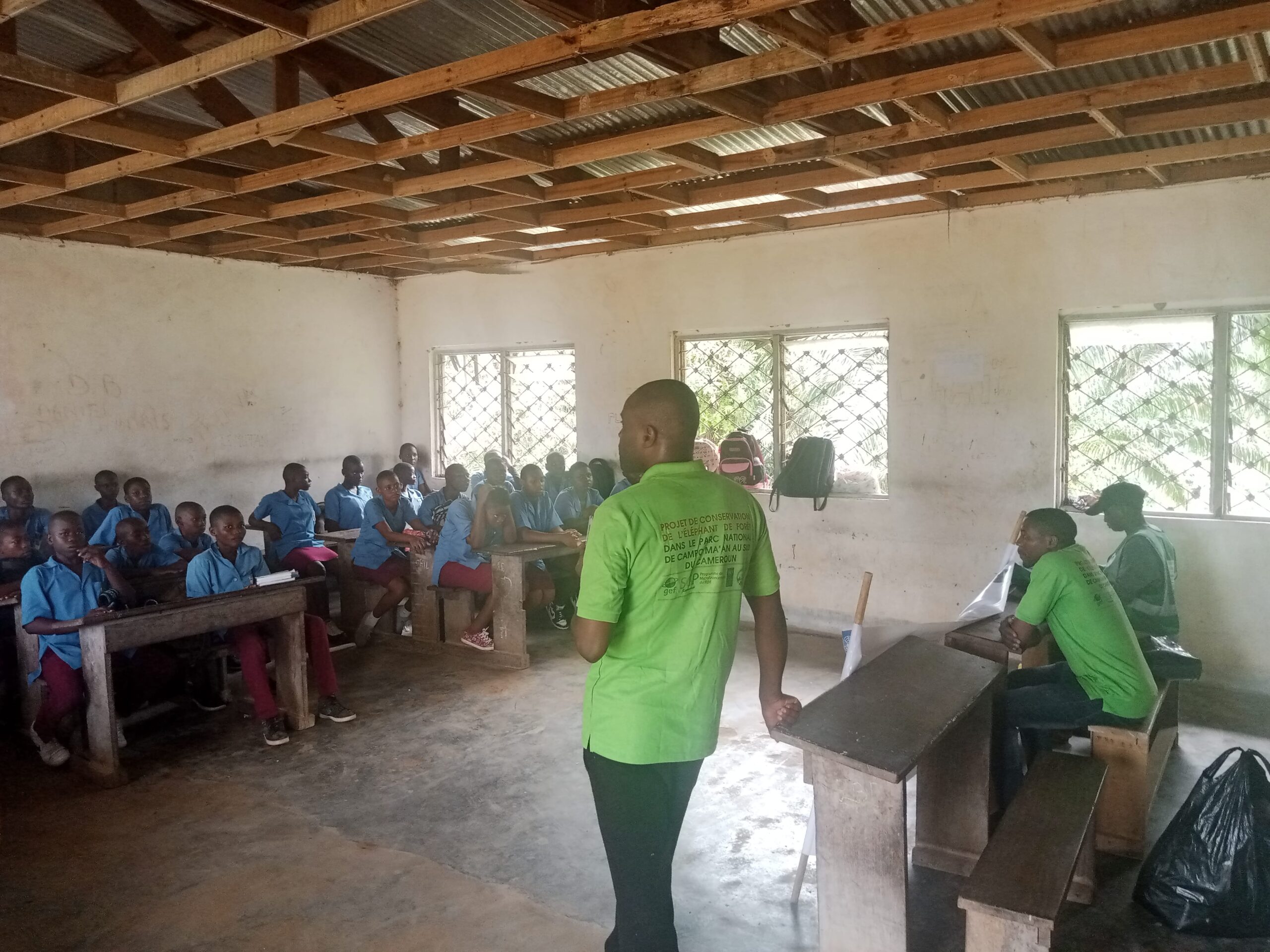
- Creation of two conservation clubs in high schools, training 138 students on biodiversity preservation.
- Formation and support of village management committees to experiment with solutions to human-elephant conflicts.
- Direct and indirect impact on 360 residents across seven villages.
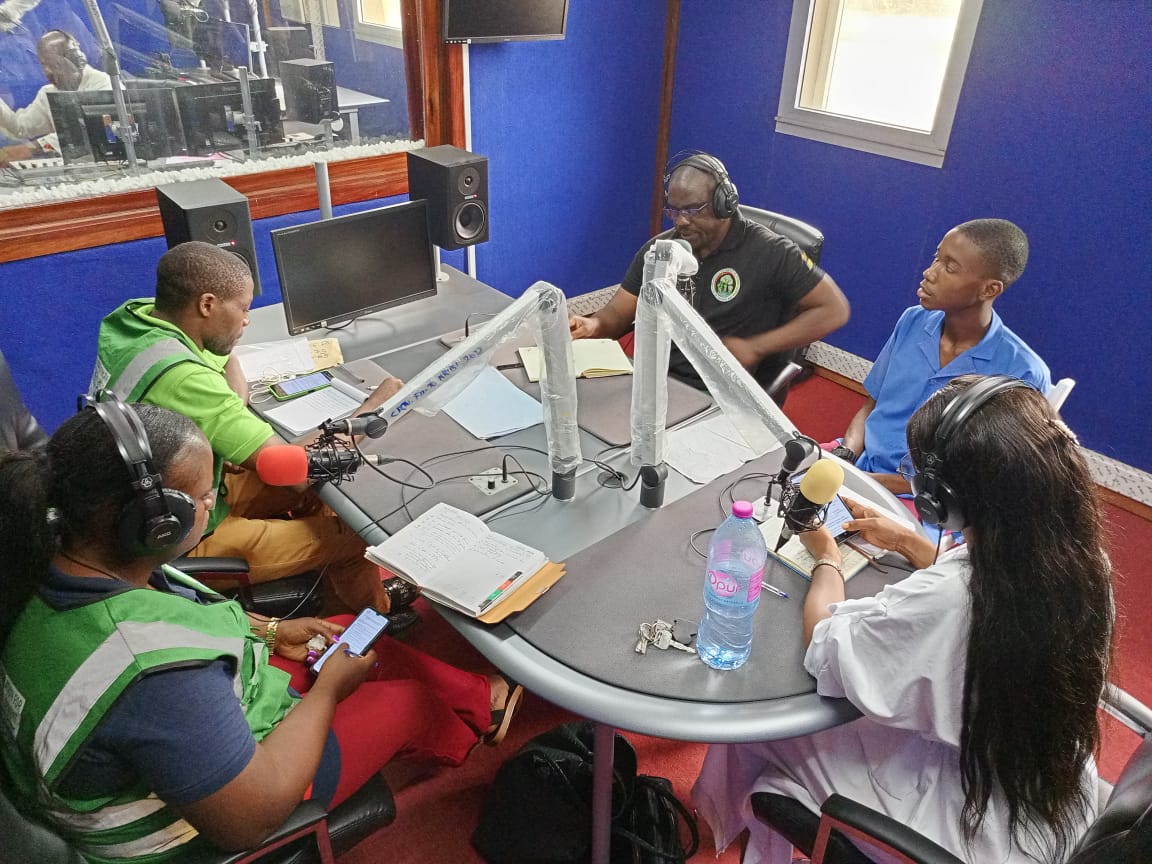
- Launch of community radio broadcasts on conservation.
PERSPECTIVES
CASuDev continues to strengthen its initiatives by collaborating with local and international partners. We remain committed to developing sustainable and inclusive approaches to protect biodiversity while supporting local populations.
SUPPORT
Join this mission or learn more about our projects by contacting us or following our activities on our website and social media. Together, let us preserve Cameroon’s natural heritage and encourage sustainable development for local communities.